Relationship Storage
BetterCRUD not only supports the query of relations, but also supports the storage of relational data, It allows you to write less boilerplate code.
For example, we have a model class
class UserBase(SQLModel):
email: Optional[str] = Field(default=None)
is_active: Optional[bool] = Field(default=True)
is_superuser: Optional[bool] = Field(default=False)
class User(UserBase, table=True):
id: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
user_name: str
hashed_password: str
profile_id: Optional[int] = Field(
default=None, foreign_key="user_profile.id")
company_id: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, foreign_key="company.id")
profile: UserProfile = Relationship(
sa_relationship_kwargs={"uselist": False, "lazy": "noload"})
tasks: List[UserTask] = Relationship(
sa_relationship_kwargs={"uselist": True,
"order_by": "UserTask.id.asc()",
"cascade": "all, delete-orphan",
"lazy": "noload"})
staff: Staff = Relationship(
sa_relationship_kwargs={"uselist": False, "lazy": "noload"})
company: Company = Relationship(
sa_relationship_kwargs={"uselist": False, "lazy": "noload"})
roles: List["Role"] = Relationship(back_populates="users", sa_relationship_kwargs={
"lazy": "noload"}, link_model=UserRoleLink)
projects: List["Project"] = Relationship(back_populates="users", sa_relationship_kwargs={
"lazy": "noload"}, link_model=UserProjectLink)
deleted_at: Optional[datetime] = Field(
default=None, sa_column=Column(DateTime(timezone=True), nullable=True)
)
created_at: Optional[datetime] = Field(
default=None, sa_column=Column(DateTime(timezone=True), nullable=True)
)
We hope to automatically store the corresponding relationship data in the post/put request body We only need to define the corresponding dto class to contain the corresponding relational data model definition
class UserCreate(UserBase):
profile: Optional[UserProfileCreate] = None
roles: Optional[List[int]] = None
tasks: Optional[List[UserTaskCreate]] = None
staff: Optional[StaffCreate] = None
projects: Optional[List[int]] = None
Your request body will include the corresponding relationship definition
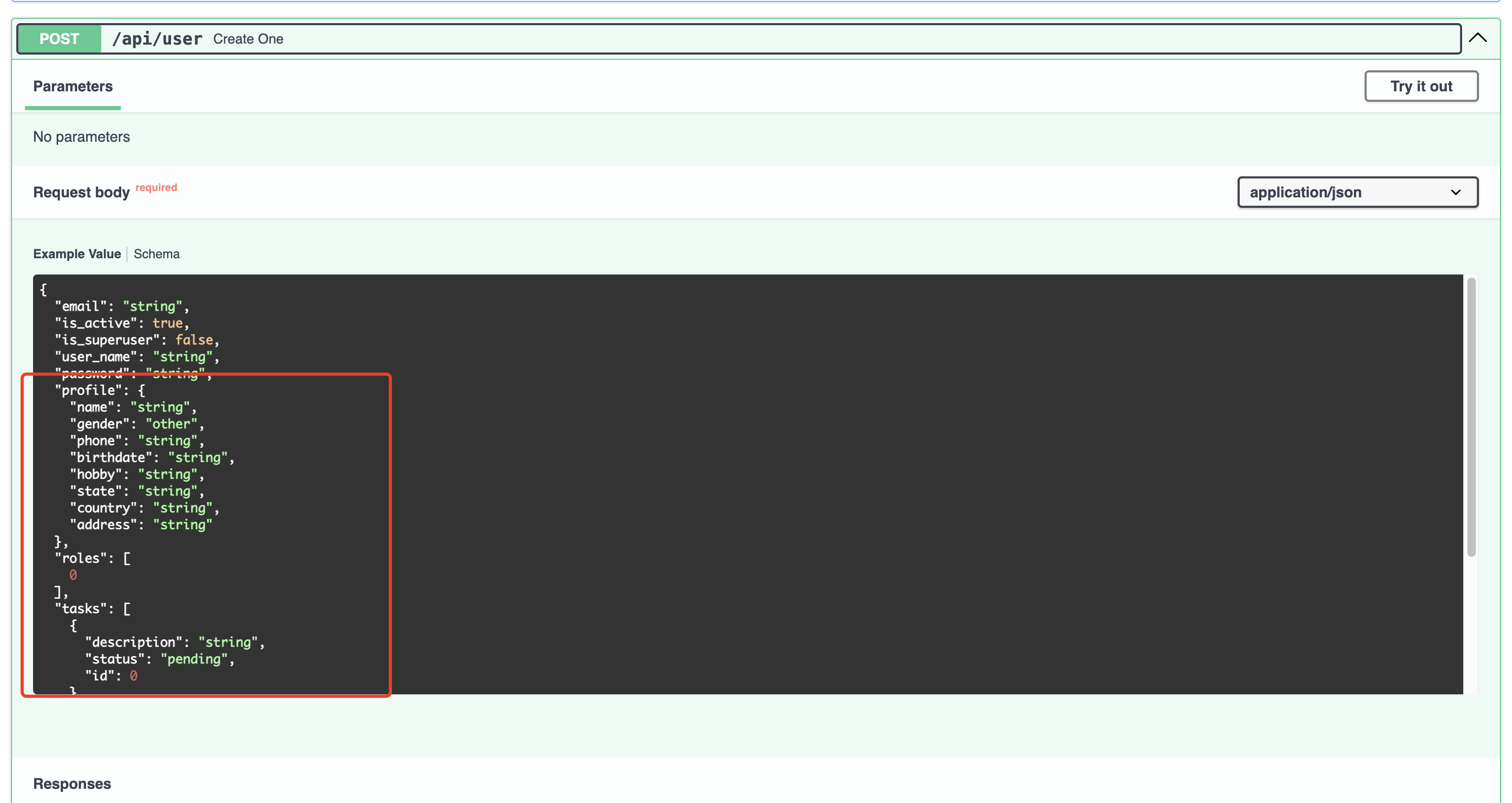
The relevant data will be stored in your database along with the request.
Magical and useful features 🤓
The following relationships are supported
- MANYTOMANY
- ONETOMANY
- ONETOONE
- MANYTOONE